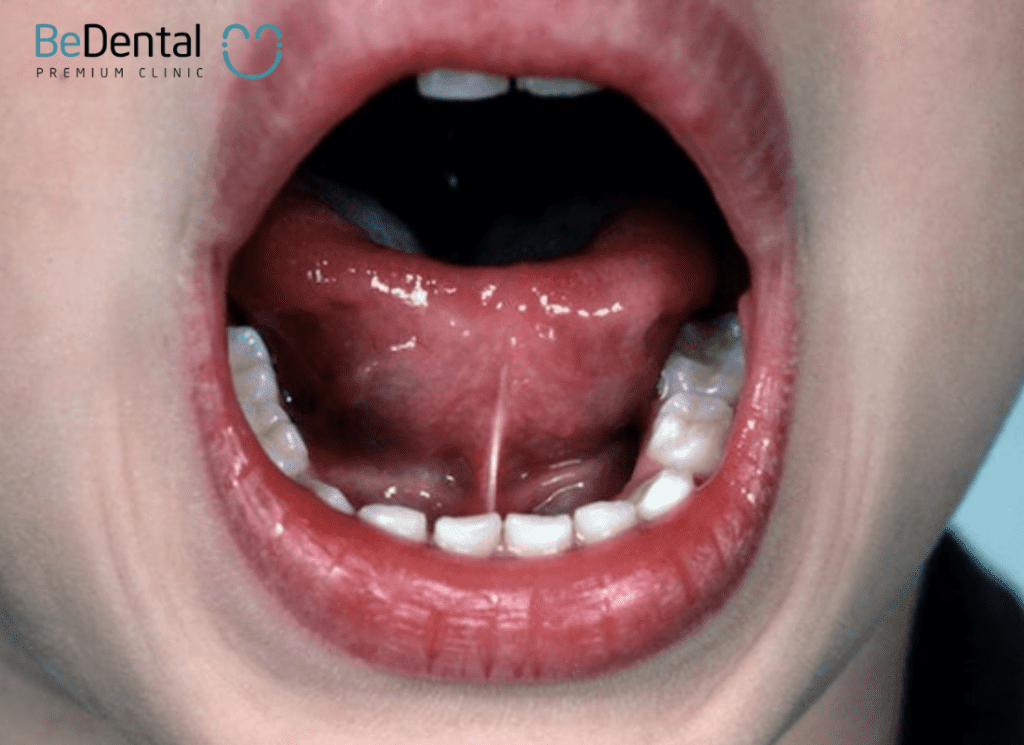
Not only children, but also many adults suffer from tongue-tie due to not receiving tongue-tie release treatment when they were young. Therefore, tongue-tie release in adults can be challenging and time-consuming. So, what are the considerations after tongue-tie release in adults? What are the THE EFFECTS OF TONGUE-TIE ? Let’s find out in the following article.
Tongue-tie in adults
Tongue-tie in adults is still a common condition. This happens because tongue-tie often develops from birth without timely treatment. Usually, people only pay attention to tongue-tied children when their tongues are swollen and consider it normal.
Adults with tongue-tie face difficulties in their daily lives, especially those with severe tongue-tie:
- Eating and tongue movements become more challenging than usual due to a short frenulum.
- They often experience speech difficulties, unclear pronunciation of sounds that require tongue movement. Additionally, many people encounter problems in their daily communication.
Due to not receiving early treatment, tongue-tie tends to develop thicker and spread, firmly attaching to the underside of the tongue and the floor of the mouth. Individuals who have had tongue-tie since childhood may experience more severe tongue-tie as they grow older..
How much does gum contouring cost? When is it recommended to undergo gum contouring?
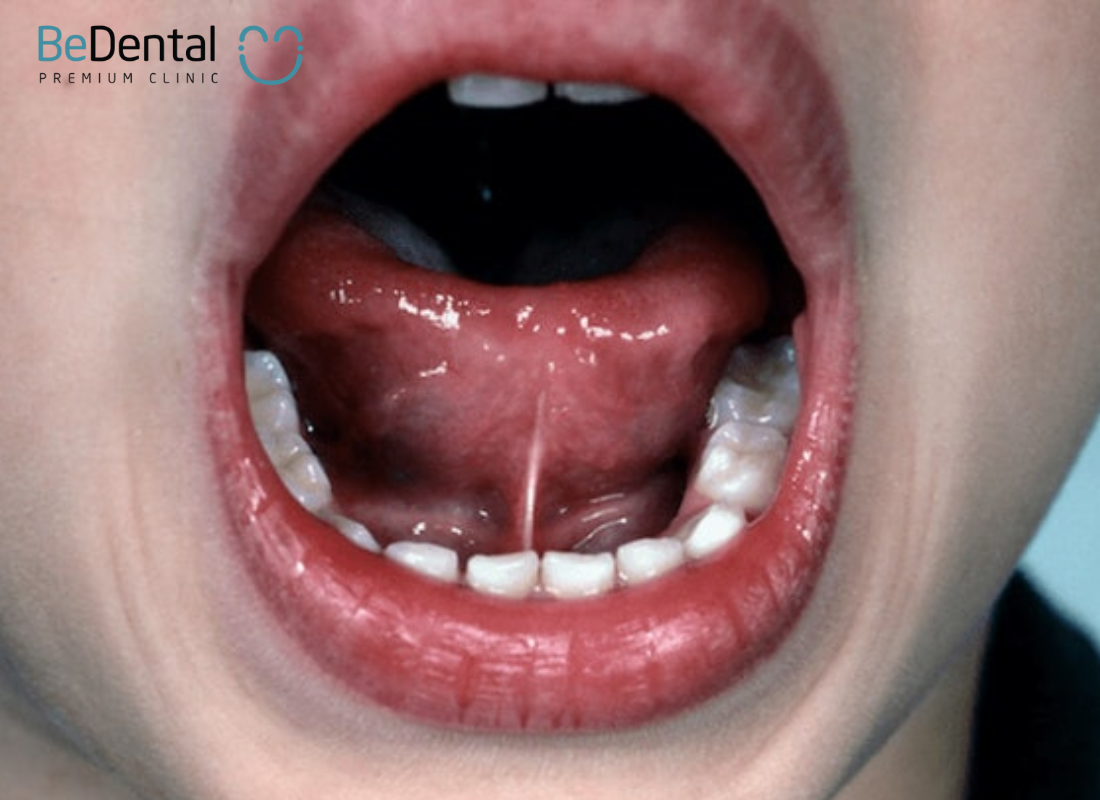
CLASSIFICATION OF TONGUE-TIE SEVERITY
According to Kotlow’s classification, tongue-tie can be categorized as follows:
- Degree I: Mild tongue-tie where the movable part of the tongue measures between 12-16mm.
- Degree II: Moderate tongue-tie where the movable part of the tongue measures between 8-11mm.
- Degree III: Severe tongue-tie where the movable part of the tongue measures between 3-7mm.
- Degree IV: Complete tongue-tie where the movable part of the tongue measures less than 3mm.
THE EFFECTS OF TONGUE-TIE
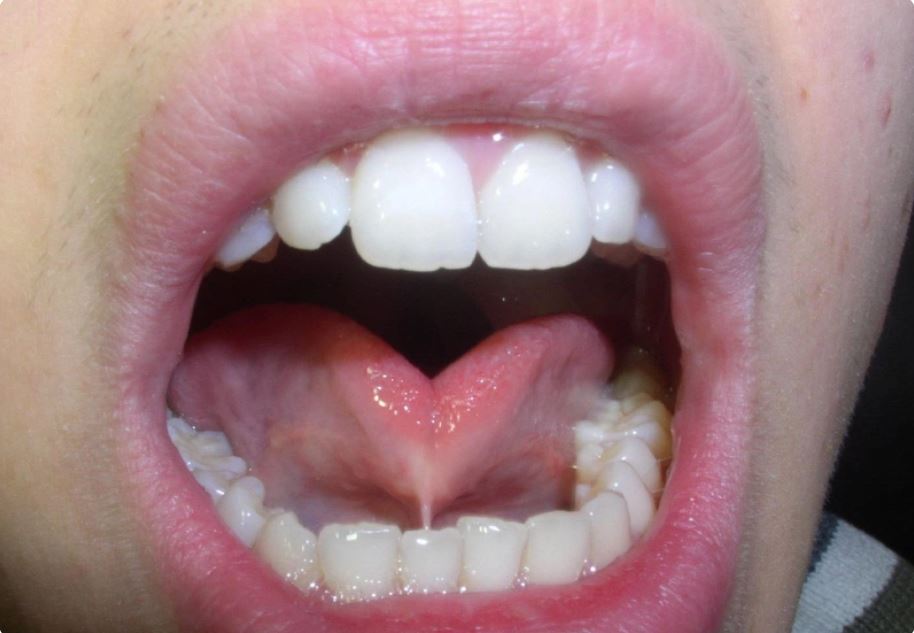
The effects of being tongue-tied include the following impacts:
- Impact on tongue mobility: In children with tongue-tie, the ability to move the tongue is restricted or extremely limited depending on the severity of the condition. The tongue cannot touch the roof of the mouth or the inner cheeks when moving from side to side.
- Impact on breastfeeding: Infants with tongue-tie may experience difficulties in breastfeeding and cause nipple pain for the mother. They may latch onto the bottle slowly, become irritable, and cry due to the inability to latch properly. As a result, these infants may gain weight slowly or not gain weight at all.
- Impact on chewing and swallowing: If the frenulum is short, the tongue faces difficulty in performing upward movements. This leads to abnormal chewing and swallowing movements and can cause an open bite. The tongue also plays a role in moving food from side to side for grinding. With a short frenulum, this function is limited, and the tongue may get bitten while eating.
- Impact on speech function: Due to reduced flexibility and difficulty in curling or protruding the tongue forward, speech function is affected. Individuals with tongue-tie struggle to articulate sounds like t, l, ch, d, r, etc. The degree of impact also depends on the age. It is more noticeable in children under the age of 5. They may have difficulty speaking, especially expressing complex sentences. In older children, the symptoms may be less pronounced, but when speaking, air may escape to the sides of the mouth.
- Impact on dental misalignment: Children with tongue-tie during the period of tooth eruption may cause tilting of the lower front teeth or create gaps between the lower front teeth. This affects aesthetics and also impacts chewing, swallowing, and speech.
- Impact on oral health: A short frenulum can cause tension and lead to inflammation and gum recession on the inner surface of the lower jaw teeth.
How is tongue-tie release performed in adults?
Unlike in children, tongue-tie release surgery in adults is performed under anesthesia, and the procedure is more complex and longer than in children.
Initial evaluation
To accurately assess the severity of tongue-tie in the patient, an initial evaluation is performed. The patient needs to undergo blood tests and consult with an anesthesiologist during the examination process.
In particular, if the patient has a tendency for difficulty in blood clotting, it needs to be communicated to the examining doctor to avoid potential risks during the surgery.
Tongue-tie release surgery
To release the tongue-tie, the patient needs to be under anesthesia throughout the procedure. Tongue-tie release surgery usually involves cutting the mucous membrane that connects the floor of the mouth and the underside of the tongue. However, in cases where the tongue-tie is not only attached at the tip of the tongue, this mucous membrane is often wide and complexly connected to blood vessels and nerves. Therefore, the tongue-tie release procedure needs to be performed with care.
Along with the tongue-tie release, the doctor also shapes the area under the tongue to ensure aesthetics and at the same time allow the tongue to function normally after the surgery without causing discomfort to the patient.
What to Do When You Have a Toothache? 9 Causes of Toothache and Treatment Methods
Postoperative care
Proper postoperative care after tongue-tie release in adults is essential.
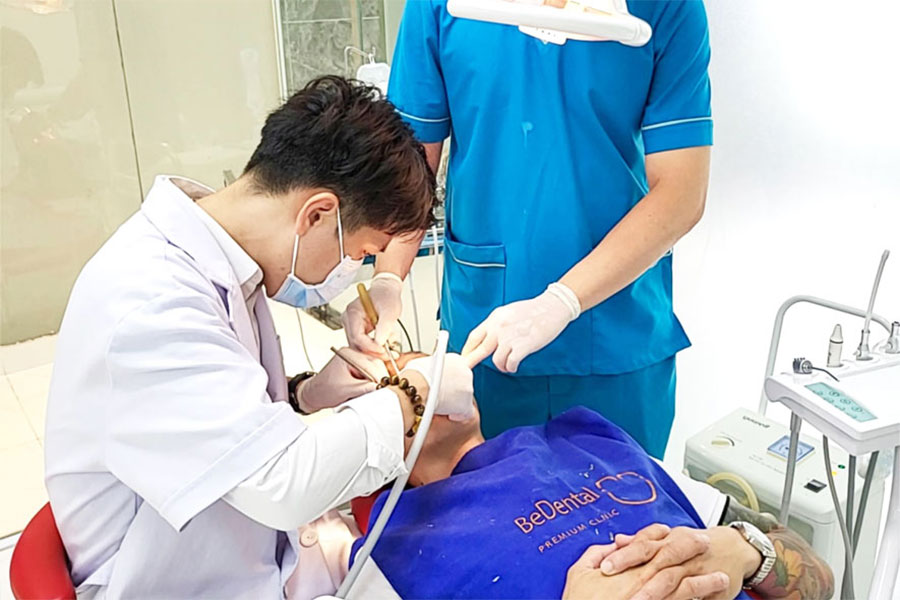
Postoperative care after tongue-tie release in adults plays an important role in achieving successful surgery. It is necessary to follow the doctor’s instructions to avoid complications after surgery.
One common complication after surgery is bleeding. Excessive movement of the tongue can cause blood vessels to rupture and result in bleeding. In the case of significant bleeding that does not stop on its own, it is necessary to seek medical intervention from a doctor.
Infection is a dangerous complication after tongue-tie release surgery. Since the tongue is located in the oral cavity, where daily intake of food occurs, eating and oral hygiene need to be followed as per the doctor’s instructions to prevent infection.
Salivary glands are located under the tongue and produce saliva in the oral cavity. Tongue-tie release surgery can affect the salivary glands. If there is swelling and pain in the area under the chin or in the throat, it is possible that the salivary glands are inflamed and damaged, and a doctor should be consulted for examination.
To achieve success after surgery, proper postoperative care is crucial and should follow the doctor’s instructions.
The postoperative care instructions after tongue-tie release in adults include:
- Limit mouth movement to avoid disrupting the wound. Avoid talking, singing, and horizontal, vertical, and twisting tongue movements to reduce the risk of bleeding.
- Ensure proper oral hygiene as instructed.
- Use medication at the correct dosage, time, and as prescribed by the doctor to prevent infection.
- Choose low-sugar and low-salt foods for eating. Avoid spicy and hot foods and consider consuming soft, cool foods like low-sugar milk. After a day, transition to eating bland, small, and cool dishes. Supplement nutrients from fruits, but choose soft varieties and cut them into small pieces to avoid tongue movements.
- Contact the doctor if there are any abnormalities and adhere to scheduled appointments.
- After the wound has healed, perform speech therapy exercises to restore normal speech. This may take time, but postoperative therapy will help you pronounce accurately and communicate confidently.
- Adults need to be patient and take care of themselves for optimal recovery.
Tư vấn chuyên môn bài viết:
BÁC SĨ DƯƠNG THỊ THÙY NGA